|
What do civil engineering students study?
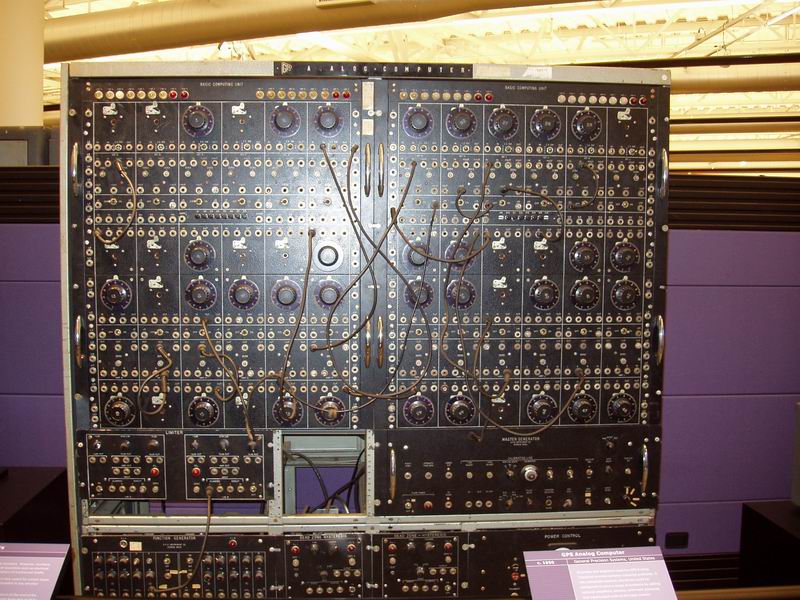

ANALOGUE COMPUTER PROGRAMMING
This course offers an introduction to the basic elements of analogue
computing and the use of such a coinputer in the solution of engineering
problems, by simulation.
The course covers the basic functional elements of an analogue con>-
puter, the basic computational functions, time and amplitude scaling
and the application of these features to the solution of a variety of
engineering problems.
APPLIED ELECTRICITY
Normal prerequisites: Mathematics I, Physics 1E.
Subject to be studied concurrently: Mathematics 11.
Electric circuit: linear and non-linear conductors, Ohm's and Kirchhoff's
Laws, power, energy. A.C. Circuits: properties, phasors, series circuits.
Machines: A.C. and D.C. generators and motors, torque and speed
characteristics, starting methods, speed conlrol. Transformers. Basic
electronics: valves. transistors, basic amplifier and rectifier circuits.
APPLIED MECHANICS IA
Statics: Equilibrium. Statically determinate trusses. Thrust, shearing
force, bending moment and torsion in statically determinate members.
Strain and Stress: Load-deflection relationships. Stress. Strain. Elastic
constants. Mohr's stress and strain circles.
Performance of Loaded Members: Stresses and deflections for simple
tension, compression bearing and shear; torsion; combined action.
(Laboratory work).
APPLIED MECHANICS IB
External Force Systems; Plane statics, loading systems, plane frames,
three dimensional force system. Dynamic systems both linear and angular,
work, power, energy and momentum.
Internal Forces: Thrust, shearing force, bending moment and torsion
diagrams.
Behaviour of Materials: Load-deflection relationships, stresses and strains.
Performance of loaded members.
APPLIED MECHANICS IIB
Performance of Loaded Members: Slope and deflection of beams. Combined
bending and torsion. Columns. Dynamics. Combined linear and
angular systems, equivalent dynamic systems, flywheels.
Machines: Power screws, clutches and brakes, belt drives, gear trains,
cams. Vibrations and Balancing.
Fluid Mechanics: Hydrostatics, perfect and real fluids. Continuity and
energy equations.

|
